
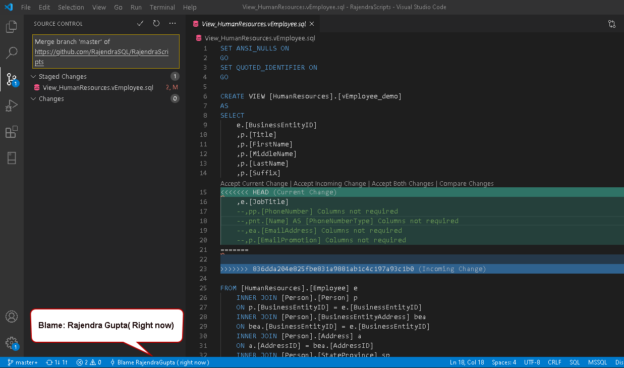
Lastly (4), in the bottom bar, you will always see the status of your current repository: active branch, incoming/outgoing changes (or a circle if there are none). You can access more specific information in other sections (3). There are a few common actions (View as Tree, Commit, Refresh, More Actions) in the top section (2). Clicking it opens a Sidebar that contains Git-related actions and views. VS Code has inbuilt Git support, which adds a Source Control tab (1) by default. The UI: There are several sections to take note of when using Git functionality through the UI. Lastly, you may execute the commands directly through the VS Code terminal (Powershell). Another way is the Command Palette (shortcut – F1), where you can search for a Git action. First, you can use the UI: buttons, menus, and tabs. There are multiple ways to perform a specific Git function within VS Code. You may refer to VS Code official documentation regarding version control for a more extensive list of features.
Synchronizing changes is a combination of push and pull.Pull changes to update your local branch with commits from remote.Push changes to add new commits from your local branch to a remote one.Synchronize – when using a remote repository, staying up to date becomes a requirement.Check out a different branch to view and work on a different version of a project.

Create a new branch so that you can work on a task without impeding others’ work.Stage changes to include in your next commit.Discard changes to undo the file’s modifications.Commit – when you make a commit, the changes you made to multiple files are grouped into a single unit and added to the project history.It creates a local repository on your device. Clone – copies a repository from GitHub, Azure DevOps, or another services provider.Here is a list of standard Git functions and how they are available: Without having any extensions installed, VS Code is sufficient for managing a local repository (cloning, branching, commits, pushing to a remote branch, etc.). Once the setup is done, you can use Git functionality within VS Code. You may refer to this blog post regarding Git setup (except for the GUI extension part). If it is not installed, some setup is required. VS Code uses your machine’s Git installation to perform version control actions. Thus, in this blog post, we will focus on using VS Code for version control purposes. For example, creating and managing pull requests within VS Code. However, if they are used, additional features become available. As a result, it is possible to perform most of Git actions without the usage of extensions. Since then, the amount of Git features and their availability has increased within VS Code. Within them, we recommended a tool called GitExtensions, for performing most Git actions. In previous blog posts, we wrote about managing AL code with Git and VS Code.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
